Concepts
While reference manual contains all the details about Jolokia protocol, configuration, agents, etc., this page highlights some high level concepts and core classes which are required to understand Jolokia goals.
Main feature
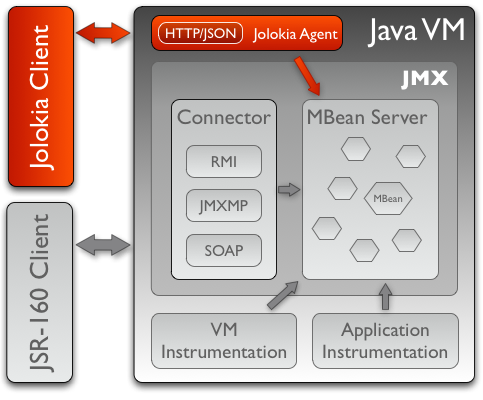
The most important feature of Jolokia is to provide a protocol adaptor for accessing MBeanServer instances and managed beans available in single or multiple JVMs.

Chapter 5.3 of JMX Specification 1.4 defines two means of remote access to JVM’s MBeanServer instances:
-
connector, which is a way to remotely expose the management interface. For RMI protocol (which is the only mandatory protocol as specified by JMX), it is a remote view of
javax.management.remote.rmi.RMIServerinterface. This approach requires active connector server running in the JVM which' MBeanServer instances we want to access remotely. -
protocol adaptor, where there is no direct remote representation of an MBeanServer. Instead a set of specific protocol operations is mapped to a set of operations on MBeanServer. For HTTP protocol, operations like GET or POST with details specified in HTTP payloads may be used to operate on an MBeanServer. And this is the approach taken by Jolokia.
|
Note
|
JMX connectors were originally defined in details in JMX Remote API Specification (JSR-160). JSR-160 was then merged with JMX Specification 1.4 (JSR-3) itself. |
Jolokia architecture
Jolokia exposes a protocol adaptor using an agent which effectively translates HTTP protocol messages into operations invoked on an instance of javax.management.MBeanServer (or javax.management.MBeanServerConnection in Proxy mode) and their results.
Each kind of Jolokia supported agent uses the same set of support classes.
Jolokia agents
There are 3 kinds of agents supported by Jolokia:
- JVM agent
-
An agent installed using JVM Attach API or Java Instrument API.
- WAR agent
-
An agent started from WAR application with
org.jolokia.server.core.http.AgentServletservlet declared. - OSGi agent
-
An agent started from a bundle, which registers
org.jolokia.server.core.osgi.OsgiAgentServletusing OSGi CMPN Whiteboard Specification for Jakarta™ Servlet.
JVM Agent uses JDK’s own HTTP server. WAR agent just runs inside Servlet container and OSGi agent uses whatever HTTP server is available in the OSGi runtime.
Jolokia support classes
For all the agents, Jolokia uses the same set of classes for two kinds of processing:
-
initialization stage, when Jolokia is configured
-
request processing stage, when Jolokia handles incoming HTTP requests, communicates with
javax.management.MBeanServerand returns HTTP responses after translating the results
Initialization stage
org.jolokia.server.core.config.Configuration-
an interface for accessing the configuration
org.jolokia.core.api.LogHandler-
an interface used for logging, delegates to underlying (Servlet, OSGi Logging,
stdout) logging mechanism org.jolokia.server.core.service.api.JolokiaServiceManager-
an interface used to configure and discover services used throughout Jolokia
org.jolokia.server.core.service.api.JolokiaContext-
single access point to access configuration, Jolokia services and register MBeans in platform MBeanServer
org.jolokia.server.core.detector.ServerDetector-
is used to detect platform-specific
javax.management.MBeanServerinstances (which may not be detected usingjavax.management.MBeanServerFactory.findMBeanServer(null))
Request processing stage
org.jolokia.server.core.service.api.Restrictor-
ACL style interface for restricting remote access
org.jolokia.server.core.http.HttpRequestHandler-
translates HTTP request into
JolokiaRequest org.jolokia.server.core.request.JolokiaRequest-
represents generic Jolokia request
org.jolokia.server.core.backend.BackendManager-
handles generic
JolokiaRequest org.jolokia.server.core.backend.RequestDispatcher-
is used by backend manager to process
JolokiaRequest org.jolokia.server.core.service.request.RequestInterceptor-
is used to process a result JSON from request dispatcher
org.jolokia.server.core.service.request.RequestHandler-
a service obtained from
JolokiaContext. Request dispatcher obtains available handlers fromJolokiaContext(andJolokiaServiceManager) and passes the incoming request to each of the handlers.
Available request handlers
Jolokia provides several implementations of org.jolokia.server.core.service.request.RequestHandler:
org.jolokia.server.core.service.impl.VersionRequestHandler-
doesn’t really call any MBean, but simply returns version information of Jolokia agent.
org.jolokia.service.jmx.LocalRequestHandler-
most important handler, which directly calls
javax.management.MBeanServer(actually a merged view of available MBeanServer instances) org.jolokia.service.jsr160.Jsr160RequestHandler-
calls remote
MBeanServerthrough JSR-160 connector (javax.management.remote.JMXConnector) org.jolokia.support.spring.backend.SpringRequestHandler-
operates on beans obtained from Spring’s
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextusingnamekey from targetjavax.management.ObjectName.